Everywhere fluently described pests for cannabis and how to deal with them, I decided to create a topic and proven methods of combating them. Therefore, please write in the comments, from what and after what helped you (drug or grandmother’s method of pest control).
Main pests of cannabis
- Decticus albifrons F.
Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa L.
Locusta migratoria L.
Calliptamus italicus L.
Kyboasca bipunctata Osh.
Empoasca flavescens F.
Hardya tenuis Germ.
Phorodon cannabis Pass.
Aphis fabae Scop.
Lygus pratensis L.
Polynierus cognatus Fieb.
Dolycoris baccarum L.
Oxythrips canriabensis Knechtel.
Melolontha hippocastani F.
Melolontha melolontha L.
Polyphylla fullo L.
Selatosornus aeneus L.
Selatosomus latus F.
Agriotes lineatus L.
Agriotes obscurus L.
Agriotes sputator L.
Melanotus brunnipes Germ.
Mordellistena micans Germ.
Mordellistena parvulieformis Stsh.
Thyetilla gebleri Fald.
Agapanthia dahli Richt.
Chaetocnema concinna March.
Psylliodes attenuata Koch.
Psalidium maxillosum F.
Lixus subtilis Sturm.
Grapholitha delineana Wkr.
Homoeosoma nebulellum Schiff.
Margaritia sticticalis L.
Ostrinia scapulalis Hbn.
Ostrinia nubilatis HB.
Acronicta rumicis L.
Agrotis segetum Schiff.
Agrotis ipsilon Hfn.
Xestia c-nigrum L.
Mamestra brassicae L.
Melanchra persicaria L.
Autographa gamma L.
Helicovera armigeraleta Hb.
Heliothis viriplaca Hfn.
Discestra trifolii Hfn.
Arctia caja L.
Vanessa urtica L.
Nymphalis polychloros L.
Tipula paludosa Meig.
Agromyza reptans Fll.
Liriornyza cannabina Hend.
Liriomyza eupatorii Kalt,
Phytornyza atricornis Mg.
Delia piatura Mg.
Whitefly
Damages tomatoes, cucumbers, patissons and pumpkins and pests for cannabis. The insect has a yellowish body and two pairs of wings densely covered with white waxy pollen.
The larva is flat, elongate-oval, pale green in color, covered with short hairs with waxy secretions, with 2 filaments at the end of the abdomen.
Females lay eggs on the underside of leaves by 10-20 eggs, placing them in the form of a ring. Larvae are sucked to leaves. The female lives for 25-30 days, laying an average of 130 eggs. Whitefly can give several generations during the season. Butterflies and larvae, sucking sap from leaves, contaminate them with sugary secretions. A sooty fungus settles on them and forms a black plaque that hinders plant development: leaves fall off, plants become depressed.
Control measures.
Traps and biological preparations “Actophyte”, “Coloracid”, “Vermicide”, Gaupsin, Actellic, Uppercut” are used
Common beetle
The larvae of this beetle damage underground parts of various plants, pests for cannabis and other root crops. Sprouts shrivel up and bald patches form in crops. Affected plants are easily pulled out of the soil and their roots are usually damaged. Bugs eat large, irregularly shaped cavities in potato tubers.

The beetle is an insect about 6 cm long and dark brown in color. The front legs are digging. The front wings are leathery, short hind wings are webbed, long, broad.
Larvae resemble adult insects: only smaller and without wings. The pest prefers light, well-watered, humus-rich or peaty soils, digging horizontal passages in them.
Larvae or adult insects overwinter at a depth of up to 70 cm. In July, females lay 200-300 eggs in the soil, from which larvae hatch. They first feed on humus and small roots, and then on plant roots.
The larvae live in the nest for the first time; later, after the first molt, they leave the nest and spread across the plot.
Control measures.
Loosening of rows at the end of May and during June to a depth of 10-15 cm to kill bear eggs.
Arrangement of trap holes.
After harvesting vegetables dig several holes 30 cm deep and 70 cm in diameter. Several shovels of manure are put in them. Finding warmer places for wintering, bears get under the manure, where they are destroyed. Among biological preparations METARIZIN is used.
From medvetka saves eggshells… when you plant seedlings add to the hole dry, crushed eggshells and mixed with soil + it is also a source of calcium and trace elements
Ticks

There is a large species diversity of mites in nature, particularly those that parasitize plants of pests for cannabis. In some cases they can cause great damage to cultivated plants. They are widespread and infest most plants.
Adults overwinter in the open ground. They reproduce all year round. One generation develops in 12-15 days. Damages leaf petioles by sucking sap from them, as a result of which they turn brown, dry out and hang down.
Control measures.
Plants are sprayed with biopreparation “Actophyte” in dilution of 40ml per 10 liters of water, alternating with “Coloradocide”.
Severely damaged plants are burned.
Kidney mite
 It develops inside blackcurrant buds, causing their overgrowth and deformation. Up to 3,000 mites and larvae accumulate in one damaged bud. Damaged buds do not develop and dry up. It is a vector of black currant fleshiness virus.
It develops inside blackcurrant buds, causing their overgrowth and deformation. Up to 3,000 mites and larvae accumulate in one damaged bud. Damaged buds do not develop and dry up. It is a vector of black currant fleshiness virus.
Control measures:
Cutting and burning of damaged branches.Early spring treatment with the preparation “Bischofit” in a dilution of 1:20 with water.
Onion root mite
Causes damage to onions in the open ground and in storage areas. Mites infest mainly damaged or diseased plants. In affected bulbs, the outer surface of succulent scales is covered with brownish cadaver, the base becomes emaciated at the edges and then falls off, roots are not formed. The female mite is short-oval, 0.5-1.1 mm long. The mite is very moisture-loving, develops in warm, humid storage conditions, especially if the onion is poured thick layer. In mature bulbs penetrates through the base. The female lays an average of 350 eggs. Larvae with three pairs of legs turn into nymphs. The mite spreads with the remains of damaged plants, soil and tools. It is introduced into the soil with damaged bulbs.
Control measures.
Deep digging of the soil. Destruction of rotten bulbs. Drying of collected bulbs at a temperature of 35-37 ° C for 5 days. Storage of onions in pre-decontaminated, well-ventilated rooms. Treatment of onion-seed before planting colloidal sulfur (40 g of the drug – per 10 liters of water; consumption – 100 ml per 1 m2). Treatment is done 20 days before harvesting onions. Also apply a solution of “Actophyte” 60ml per 10 liters.
Spider mite infestations
It infects pepper, eggplant, cucumber, pumpkin, beet, dill, parsley and peppermint, pests for cannabis, as well as various fruit plants by sucking juice from the underside of leaves. It is a small arthropod with yellowish-green or orange-red color. During the growing season, the mite gives up to 12 generations and causes considerable damage to agriculture.
Control measures.
1 cup of garlic (or onion) and dandelion leaves put through a grinder and 1 tbsp. of liquid soap diluted in 10 liters of water. Strain, separating the pulp, and spray plants in any phase of development. But more effective pollination of plants with ground sulfur (30 g per 10 m2), no more than 5 times per vegetation.
In addition, excellent results gives application of the preparation “Bischofit” in dilution 1:20 on dormant buds, 1: 80 povergetiruyuschih plants in the summer. Also the use of biological preparations “Actophyte”, Coloradocide” during the growing season.
Preparations: Aktellik, Uppercut, Fitoverm.
Common earwig
Damages various vegetable crops. Adults and larvae eat leaf edges, petals and inner parts of flowers. They feed at night; during the day they hide under clods of earth, stones, leaves, etc.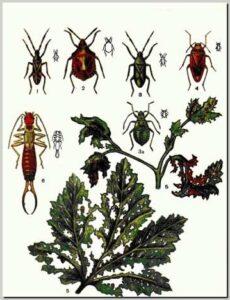
The earwig has a flat brown body 9.5-16 mm long. It winters under stones, in soil, in crevices of greenhouses, etc. In April-May females lay eggs in the soil; larvae emerge in May.
Control measures.
Removal of plant residues, destruction of weeds. If a large number of insects appear, it is recommended to spread wet rags or leaves in between the rows and destroy the earwigs hiding there with boiling water.
In addition, excellent results give the use of biological insecticides; “Aktofit” “Vermicide”, “Coloradocide”
Bedbugs
Sucking insects with incomplete transformation. They have a peculiar peculiarity to secrete a foul-smelling liquid with special glands, which serves as a means of defense. Quite small insects sucking sap from plants. Widespread everywhere. Adult insects overwinter under leaves, plant residues and in other secluded places.
Control measures:
Removal of plant residues, destruction of weeds.Application of biological insecticides “Aktofit” “Vermicide”, “Coloradocide”
Miner
Affects lettuce plants. The larvae make mines in the leaves; at the end of the mines, a larva or pupa can be found.
The larva has a white-gray body 3 mm long, without legs and head. Pupae in a yellow-brown false cocoon overwinter in the soil. The insects are two-winged individuals up to 2 mm long, with a large thorax and a black, shiny, 6-segmented abdomen. Females lay eggs in leaf pulp. The development period of one generation is 18-24 days.
Other species of miners are widespread not only on vegetable crops, but also on ornamental crops.
Control measures.
Elimination of weeds. Removal of damaged leaves. Disinfection of soil in greenhouses.In addition, the use of “Vermicide” gives good results
Onion moth miner
Causes great damage to onions in warm, dry weather. Damaged leaves, starting from the tops, turn yellow and dry up. They show light longitudinal, irregularly shaped spots – mines.
The caterpillars of the first generation are harmful in May-June. Moths are small (wingspan 12-14 mm).
They fly at night in July. Females lay single, yellowish eggs about 0.5 mm in size at the base of leaves (and sometimes near the plant) on the soil surface. Caterpillars are yellow-green, 8-11 mm long, with brown warts. They penetrate the leaves and feed on them. In late September – early October, butterflies emerge from pupae and overwinter in various sheltered places, plant residues.
Control measures.
Observance of crop rotation. Feeding plants with nutrients. Destruction of plant residues. Autumn digging of the soil.
Preparation uppercut, actellik, actophyte
Beet fly
Causes considerable damage to all beet species. The larvae are legless, yellowish, 7-8 mm long. The larvae eat wide passages (mines) in leaf parenchyma, resulting in leaf spots. At first they are pale, later they turn brown, dry up and fall out, and leaves become holey.
Female flies lay eggs, singly or in small groups, on the underside of leaves. The hatched larvae penetrate into their tissues.
Two generations usually develop during the summer: the first one flies during cherry blossom, the second one – in July.
Control measures.
Treatment of beet with the preparation “Actophyt”, “Coloracid, Uppercut, Actellik”
Observance of crop rotation. Deep digging of the soil in the fall. Frequent loosening of rows with the addition of repellent substances (powder of ground pepper, mustard, wood ash).
Aphids
 Pests for cannabis and if preventive measures are not taken in time to limit their development, the damage caused by aphids can reach 80%. Aphids damage peppers, zucchini, patissons, pumpkins, cabbage, turnips, spinach and peppermint. It damages shoots, flowers, ovaries and leaves. Appears in the second half of summer. At first the aphid is yellowish, then dark green. This pest develops very quickly and in just a few days envelops the entire underside of the leaves, causing them to curl.
Pests for cannabis and if preventive measures are not taken in time to limit their development, the damage caused by aphids can reach 80%. Aphids damage peppers, zucchini, patissons, pumpkins, cabbage, turnips, spinach and peppermint. It damages shoots, flowers, ovaries and leaves. Appears in the second half of summer. At first the aphid is yellowish, then dark green. This pest develops very quickly and in just a few days envelops the entire underside of the leaves, causing them to curl.
Control measures.
When aphids appear, plants are sprayed with pepper infusion: 50 g of crushed fresh bitter pepper, 1 tbsp. spoon of liquid soap, 2-4 tbsp. spoons of wood ash diluted in 10 liters of warm (60 ° C) water. The solution is infused for 1 day and then strained. The treatment is repeated in 5-6 days.
Ash solution is also effective: 2 cups of wood ash are poured with hot (70-80°C) water, 2 tbsp. of liquid soap are added and infused for 1 day. Before spraying the solution is strained.
The procedure is carried out in warm weather, in the evening.
Among biological preparations the application of Aktellik, “Aktofit” preparations in alternation with “Coloracid”, “Vermicide”, “Guapsin” preparations gives good effect.
In addition, it is obligatory to take appropriate measures to limit the spread of ants.
Sowki
 There is a large number of these insects (more than 2000 thousand species only in our climatic zone). All of them are large butterflies with different coloration of wings Wingspan – 34-45 mm.
There is a large number of these insects (more than 2000 thousand species only in our climatic zone). All of them are large butterflies with different coloration of wings Wingspan – 34-45 mm.
Caterpillars are 50 mm long, earthy-gray, green or other color with glossy skin; they overwinter in the soil at a depth of 10-25 cm. Butterflies fly in July (evening and night), feeding on nectar of flowering plants. The pest lays eggs one by one or several (from 470 to 2200 eggs in total) on the underside of leaves adjacent to the ground. Caterpillars develop in the soil, damaging seeds and seedlings, gnawing plants at ground level, eating leaves by dragging them into the soil.
into the soil.
Potato scoop
Gnaws holes in the stems, rhizomes and leaf petioles of plants such as sorrel and rhubarb. The caterpillars pupate in the soil. The adult caterpillar, which is light yellow or grayish-brown with a reddish stripe along the back, is about 5 cm long. Larvae hatch from eggs in spring. They feed on weeds of the cereal family.
Control measures.
Deep fall digging of the soil. Destruction of weeds. Excellent results are obtained by the use of biological preparations “Vermicide” (lepidocide), “Actophyte”, “Guapsin”, “Coloracid, Actellic, Uppercut”.
Spraying is carried out at intervals of 7-10 days. In addition, it is recommended to use mixed plantings, as well as planting spicy plants between growing crops. The use of pheromone and light traps gives good results.
Hemp leafhopper
Pests for cannabis the latin name is Grapholitha delineana Walk. Pest outbreaks can be found in any cannabis-growing area.
The moth reaches a wingspan of 15 mm; its forewings are brown with oblique yellowish strokes; its hind wings are gray. The caterpillar of the leafhopper is about 8 mm long, greenish or pink.
These caterpillars overwinter in their spider cocoons, which are located in the soil at a depth of about 5 cm or live under plant debris.
 In spring, the caterpillar leaves its cocoon and pupates on the soil surface. After one or two weeks it begins to fly. Insects become more active at night or in the black. Female leafhoppers lay one or several eggs on hemp stems and leaves.
In spring, the caterpillar leaves its cocoon and pupates on the soil surface. After one or two weeks it begins to fly. Insects become more active at night or in the black. Female leafhoppers lay one or several eggs on hemp stems and leaves.
The fecundity of these insects is 80-500 eggs. After 10 days, the caterpillars begin to skeletonize the hemp leaves they encounter, braiding them with webs on the underside. Older caterpillars damage leaf petioles and gnaw out entire passages in the stems: small but visible thickenings are formed where they are inserted. The development of caterpillars lasts about four to five weeks, and they pupate inside the cannabis stem or in the soil itself. The moths, which emerge 14 days later, lay eggs on inflorescences and hemp stalks.
The caterpillars of the second generation of leafhoppers eat the inflorescences, causing the plant to shrivel up, and they also damage unripe hemp seeds. As many as three generations of this pest can develop during the growing season.
Control methods:
Pesticides should be selected for hemp against leafhopper. Conduct spring soil loosening. Spatially isolate new crops from last year’s crops. Collect and destroy all plant residues. All this will significantly reduce the number of the pest.
Preparations: Actophyte, Actellik, Uppercut.
Naked slugs
Control measures.
Pests for cannabis to protect plants from naked slugs, the soil around plants is pollinated with ground superphosphate, potassium salt, lime fluff or wood ash (200-300 g/m2) twice, in 20-30 minutes, better after sunset.
To collect slugs among strawberry bushes spread leaves of burdock, cabbage and other plants, as well as wet boards and rags. Slugs crawl under them, after which it is easier to collect and destroy them
 Preparations: Thunderstorm
Preparations: Thunderstorm
Snails
Multivorous pests that damage not only above-ground but also underground pests for cannabis, red cabbage, cauliflower, sorrel and pepper. Their appearance is recognized by the eaten leaves and the traces left behind – silvery dried mucus.
Control measures.
On a half-liter jar of wood ash – 1 tbsp. spoon of table salt, ground pepper (black or red) and dry mustard. Everything is thoroughly mixed. On a hot sunny day this mixture pollinate the soil between the rows of plants and immediately loosen it to a depth of 3-5 cm, because it is in this layer in the daytime hiding pests. Slugs and snails on the soil surface after loosening dry out and die.
On the same day in the evening do a second treatment: on a half-liter jar of wood ash add 1 tbsp. spoon of ground pepper or dry mustard, all mixed and through a gauze bag, pollinate plants.
Preparations: Thunderstorm
Nematodes
 A roundworm whose larvae damage potato roots and pests for cannabis. During flowering and later, poppy seed-like cysts can be found on the roots of affected plants. Each of them contains from 200 to 1000 eggs with larvae. The cysts remain viable in the soil for up to 10 or more years. Affected plants lag behind in growth and development; lower leaves die off, the rest wither and turn yellow.
A roundworm whose larvae damage potato roots and pests for cannabis. During flowering and later, poppy seed-like cysts can be found on the roots of affected plants. Each of them contains from 200 to 1000 eggs with larvae. The cysts remain viable in the soil for up to 10 or more years. Affected plants lag behind in growth and development; lower leaves die off, the rest wither and turn yellow.
Control measures.
Observance of quarantine and prophylactic measures: do not use infected seeds and soil cultivation tools. Cereals, leguminous or vegetable crops should be cultivated in the affected areas for 3-4 years, and then nematode-resistant vegetable varieties should be grown.
Among biological preparations, “Nematophagin” and promising preparations based on predatory nematodes, which are currently under development, can be used.
Thrips
 Small insect, about 1 mm long, light yellow or dark brown. Larvae are wingless, whitish or greenish-yellow. They damage onions by sucking sap from leaves and inflorescences, resulting in stunted growth and wilted leaves. Thrips overwinter in plant debris, under dry onion scales, and in the upper layer of soil. Females lay small brownish eggs, placing them singly under the skin in leaf tissue.
Small insect, about 1 mm long, light yellow or dark brown. Larvae are wingless, whitish or greenish-yellow. They damage onions by sucking sap from leaves and inflorescences, resulting in stunted growth and wilted leaves. Thrips overwinter in plant debris, under dry onion scales, and in the upper layer of soil. Females lay small brownish eggs, placing them singly under the skin in leaf tissue.
Control measures.
Crop alternation; disinfection of bulbs before planting with hot (45°C) water for 10 min followed by cooling with cold water.
Apply “Actophyte”, “Vermicide, Actellik”. In addition, the use of “Boverin” and special glue traps gives good results
Hemp flea
Pests for cannabis occurs everywhere, especially harmful in industrial hemp growing areas. Damages hemp and hops.
 The beetle is 1.8-2.6 mm in size, green-bronze, antennae with 10 segments, tibiae, legs and elytral tips red, frontal lines distinct. Egg is oval, 0.4 mm in size, clear yellow. Larva – 3-3.5 mm, yellow-white, thin, oblong, chair distinctly separated, body surface covered with sclerites having bristles, chair, first thoracic and last abdominal segments yellow-brown.
The beetle is 1.8-2.6 mm in size, green-bronze, antennae with 10 segments, tibiae, legs and elytral tips red, frontal lines distinct. Egg is oval, 0.4 mm in size, clear yellow. Larva – 3-3.5 mm, yellow-white, thin, oblong, chair distinctly separated, body surface covered with sclerites having bristles, chair, first thoracic and last abdominal segments yellow-brown.
Immature adults overwinter on hemp or in places with woody and shrubby vegetation in the soil, at a depth of 10-15 cm. They withstand temperature drop to – 25 °С, emerge from hibernation sites in April, additionally feed on nettle and hop leaves, then migrate en masse to hemp ladder. After additional feeding, which lasts 12-15 days, adults mate and start laying eggs in the soil at a depth of 8-10 cm. Fecundity is up to 300 eggs. Larvae revived in 6-20 days feed on roots for 21-40 days. They pupate in the soil at a depth of 1 to 8-10 cm. Pupa develops from 6-7 to 15 days. Adults feed on upper leaves and eat underdeveloped seeds before going into winter (September). After harvesting, they continue to feed on the skin of the stalks and stubble.
Damage is caused by adults and larvae. Adults gnaw small through holes in seedlings and later in true leaves, gnaw stems of seedlings near the soil surface. Larvae nibble roots.
Control measures. Collection and burning of post-harvest residues. Destruction of cannabis seedlings and weeds. If the number of adults is 15 per 10 plants – insecticide treatment of hemp seedlings.
